Finance Commission
The Finance Commission is a constitutional body tasked with allocating specific financial resources between the Union and the states. It was established under Article 280 of the Indian Constitution by the Indian President. It was established to define the Centre’s and the states’ financial relationships. It was established in 1951.
Article 280 of the Indian Constitution
- President after two years of the commencement of Indian Constitution and thereafter every 5 years, has to constitute a Finance Commission of India.
- It shall be the duty of the Commission to make recommendations to the President in relation to the:
- the distribution between the Union and the States of the net proceeds of taxes which are to be, or maybe, divided between them and the allocation between the States of the respective shares of such proceeds;
- the principles which should govern the grants in aid of the revenues of the States out of the Consolidated Fund of India;
- any other matter referred to the Commission by the President in the interests of sound finance
- The Commission shall determine their procedure and shall have such powers in the performance of their functions as Parliament may by law confer on them
Note: President can also constitute Finance Commission before the expiry of five years as he considers necessary
Article 281 of the Indian Constitution
- It is related to the recommendations of the Finance Commission:
- The President has to lay the recommendation made by Finance Commission and its explanatory memorandum before each house of Parliament
Finance Commission Chairman and Members
- Chairman: Heads the Commission and presides over the activities. He should have had public affairs experience.
- Four Members.
- The Parliament determines legally the qualifications of the members of the Commission and their selection methods.
Qualifications of Finance Commission Chairman and Members
- The 4 members should be or have been qualified as High Court judges, or be knowledgeable in finance or experienced in financial matters and are in administration, or possess knowledge in economics.
- All the appointments are made by the President of the country.
- Grounds of disqualification of members:
- found to be of unsound mind, involved in a vile act, if there is a conflict of interest
- The tenure of the office of the Member of the Finance Commission is specified by the President of India and in some cases, the members are also re-appointed.
- The members shall give part-time or service to the Commission as scheduled by the President.
- The salary of the members is as per the provisions laid down by the Constitution.
Functions of Finance Commission
The Finance Commission makes recommendations to the president of India on the following issues:
- The net tax proceeds distribution to be divided between the Centre and the states, and the allocation of the same between states.
- The principles governing the grants-in-aid to the states by the Centre out of the consolidated fund of India.
- The steps required to extend the consolidated fund of a state to boost the resources of the panchayats and the municipalities of the state on the basis of the recommendations made by the state Finance Commission.
- Any other matter referred to it by the president in the interests of sound finance.
- The Commission decides the basis for sharing the divisible taxes by the centre and the states and the principles that govern the grants-in-aid to the states every five years.
- Any matter in the interest of sound finance may be referred to the Commission by the President.
- The Commission’s recommendations along with an explanatory memorandum with regard to the actions done by the government on them are laid before the Houses of the Parliament.
- The FC evaluates the rise in the Consolidated Fund of a state in order to affix the resources of the state Panchayats and Municipalities.
- The FC has sufficient powers to exercise its functions within its activity domain.
- As per the Code of Civil Procedure 1908, the FC has all the powers of a Civil Court. It can call witnesses, ask for the production of a public document or record from any office or court.
Advisory Role of Finance Commission
The Finance Commission’s recommendations are solely advisory in nature, and hence are not binding on the government. It is up to the government to put its suggestions on allocating money to states into action. In other words, “it is nowhere stated in the Constitution that the Commission’s recommendations should be obligatory upon the Government of India or that it would amount to a legal right favouring the recipient states to receive the money proposed by the Commission.”
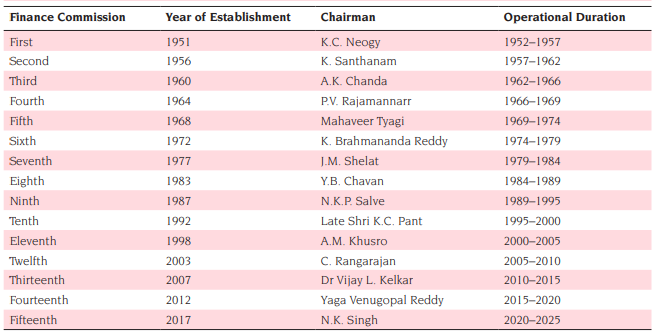
List of Finance Commissions