UK Assistant Prosecution Officer APO Exam Syllabus
UK Assistant Prosecution Officer APO Exam will be conducted in two phases.
- Preliminary Examination
- Mains Examination
- Written Exam
- Interview
Preliminary Examination
| S. No. | Subject | Max. Marks | Questions | Time |
| Paper I | General Studies | 100 | 100 | 1 : 30 hrs |
| Paper II | Law | 100 | 100 | 1 : 30 hrs |
| Total Marks | 200 |
Mains Examination
| S. No. | Subject | Max. Marks | Questions | Time | Level | Comment |
| I | General Studies | 100 | 10 | 03 : 00 hrs | General | |
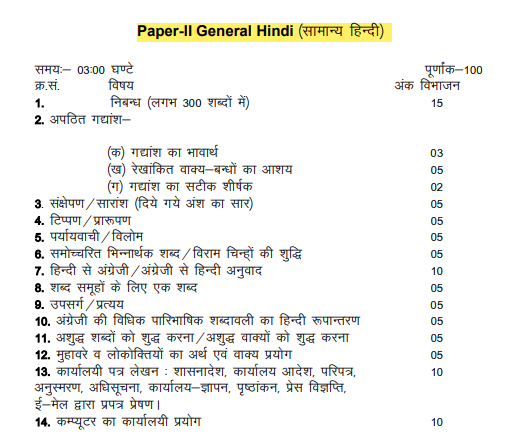
| II | General Hindi | 100 | 14 | 03 : 00 hrs | High School | Min. 35 marks |
| III | Law-I (Criminal Law and Procedure with Police Act | 100 | 10 | 03 : 00 hrs | Law Graduate | |
| IV | Law-II Evidence Act | 100 | 10 | 03 : 00 hrs | Law Graduate | |
| Total Marks | 400 |
Interview : 50 Marks
Syllabus for Assistant Prosecution officer (APO) Preliminary Examination
There will be two papers in preliminary examination.
Paper-1 General Studies
Time – 01:30 hrs, M.M 100
Total number of questions 100 in General Knowledge (Objective Type)
The paper on General Knowledge will include the following topics, besides day to day happenings around India and the world. Candidates are expected to have general awareness about the following:
(a) General Science
(b) Current events: National and International
(c) History of India
(d) Indian National Movement and Indian Polity
(e) Geography and Indian Economy
(f) Art, Culture and Traditions of Uttarakhand
(g) Revenue Police System and general administrative set up in Uttarakhand
(h) Forest, Crops, Tribes, Mountains, Rivers of Uttarakhand.
Questions on General Science: Will cover elementary Knowledge & understanding of science including matters of everyday observation and experiences, basic laws of science, questions pertaining to environmental factors, natural resources, food crops, biosphere, human diseases,
flora and fauna, national parks and wildlife of Uttarakhand will also be included.
Current events: Day to day happenings in India and around the world, which will also include significant events including sports.
History Of India: Emphasis should be on broad understanding of social, economic and political aspects of India.
Indian National Movement: The candidate should be aware of the Freedom Movement, Growth of Nationalism and attainment of Independence.
Indian Polity (Post Independence): Questions will test Knowledge of country’s political system including Panchayati Raj and Community Development.
Geography and Indian Economy: Only general understanding of the subject will be expected.
Culture and Traditions of Uttarakhand: The candidate should be aware of the culture and traditions, especially of tribes of Uttarakhand.
Revenue Police and special administrative system of Uttarakhand: Power and functions of Patwaries, Kanoongos and Naib Tahsildars etc. Panchayati Raj system, Van-Panchayat System. Candidates should be aware of types of forests, rotation of crops, cultural festivals, prominent holy places, glaciers and mountains, natural resources and calamities, rivers & lakes as well as prominent personalities of Uttarakhand.
Paper- II Law
Time – 01:30 hrs M.M 100
Total number of questions 100 On Law (Objective Type)
It will cover the following with the number of questions indicated as under Topics No. of questions
| S. No. | Subject | Max. Marks |
| 1. | The Indian Penal Code | 35 |
| 2. | The Indian Evidence Act | 25 |
| 3. | The Code of Criminal Procedure | 25 |
| 4. | The Uttarakhand Police Act, 2007 | 15 |
| Total | 100 |
The Indian Penal Code, 1860:
i) General Exceptions
ii) Joint and Constructive Liability
iii) Abetment
iv) Criminal Conspiracy
v) Offences against Public Tranquility
vi) Offences against human body: Culpable homicide and murder including causing death by negligence; hurt and grievous hurt; wrongful restraint and wrongful confinement; criminal force and assault; kidnapping and abduction.
vii) Offence against women: sexual offences; offences relating to marriage, cruelty by husband or relatives of husband; insult to modesty of a woman and dowry death.
viii) Offences against property: Theft, Extortion, Dacoity, Robbery, Criminal Misappropriation, Cheating, Mischief and Criminal Trespass.
ix) Attempts to commit offences.
The Indian Evidence Act:
i) Relevancy of facts: Definitions, Relevancy of facts, Admission & Confession, Dying Declaration, Opinion of third persons when relevant.
ii) Facts which need not be proved: Oral and documentary evidence, Exclusion of oral by documentary evidence, Public documents and presumption as to documents.
iii) Production and effect of evidence: Burden of proof, Estoppel, Witnesses including their examination.
Criminal Procedure Code, 1973
Constitution, Powers and jurisdictions of Criminal Courts; Arrests, Power to compel appearance of persons and production of things; Maintenance of public order and public tranquility; Initiation and commencement of proceedings before Magistrate; Framing of
charges; Trial of cases; Judgment; Evidence in enquiries and trials; Bail and Bonds; Reference, Revision and Appeal.
The Uttarakhand Police Act, 2007
i) Powers, functions and duties of various police officers under the aforesaid Police Act.
ii) Duties of Officer-In-Charge of police station regarding reports made at police stations; Investigation, Arrest, Bail and Custody and Execution of processes.
iii) Powers, functions and duties of Public Prosecutors and their sub-ordinates.
Syllabus for Main Examination